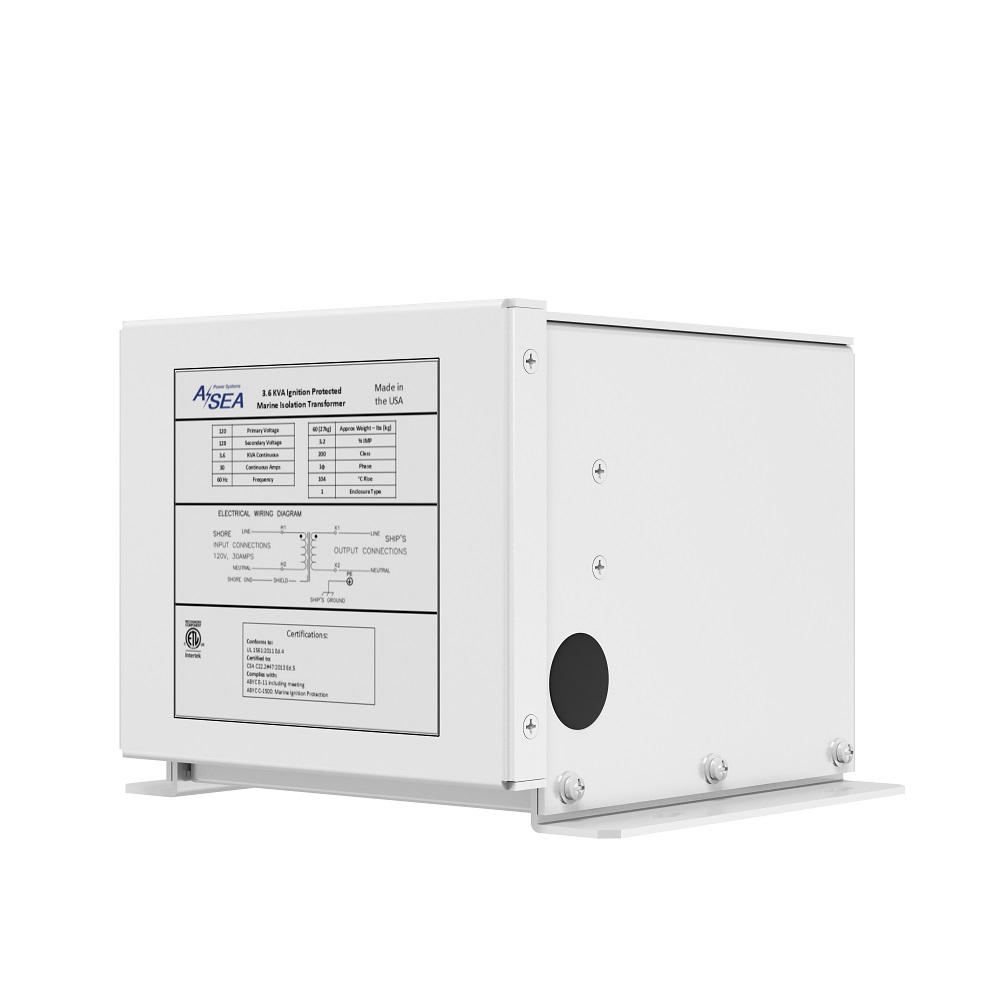
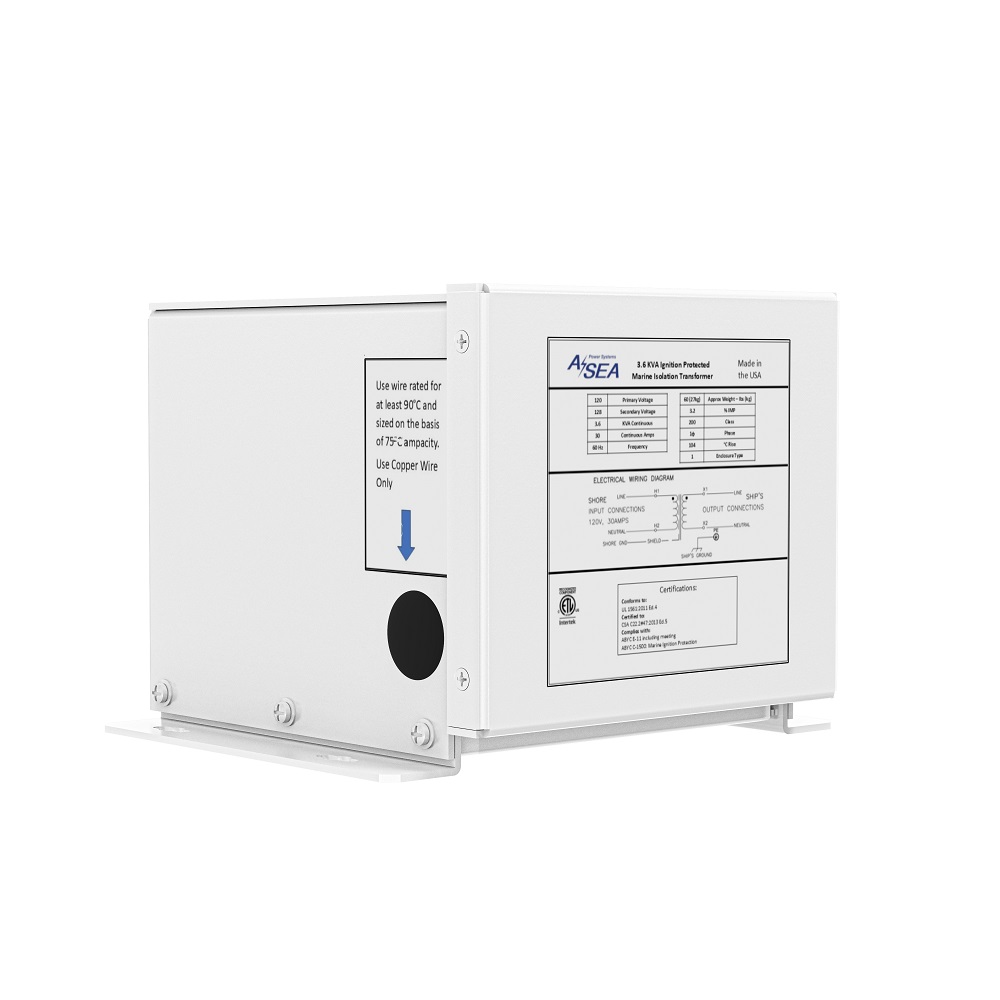
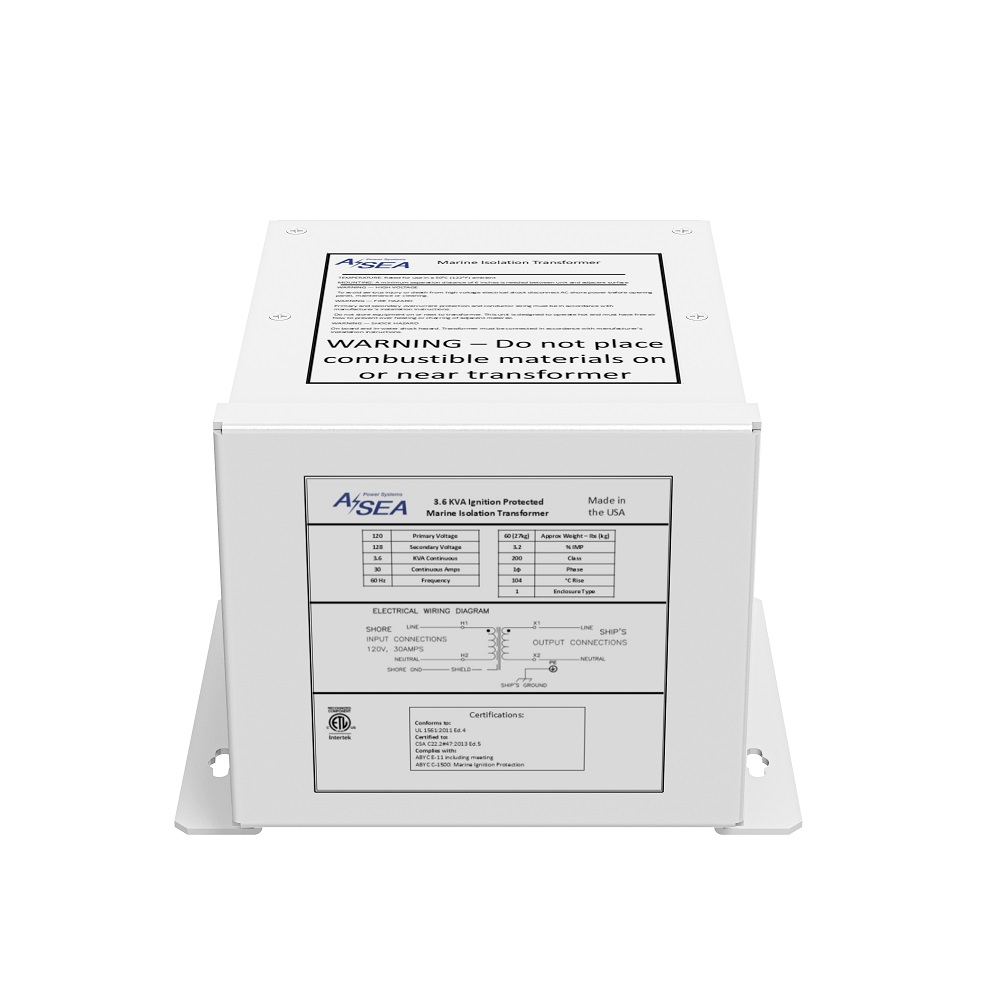
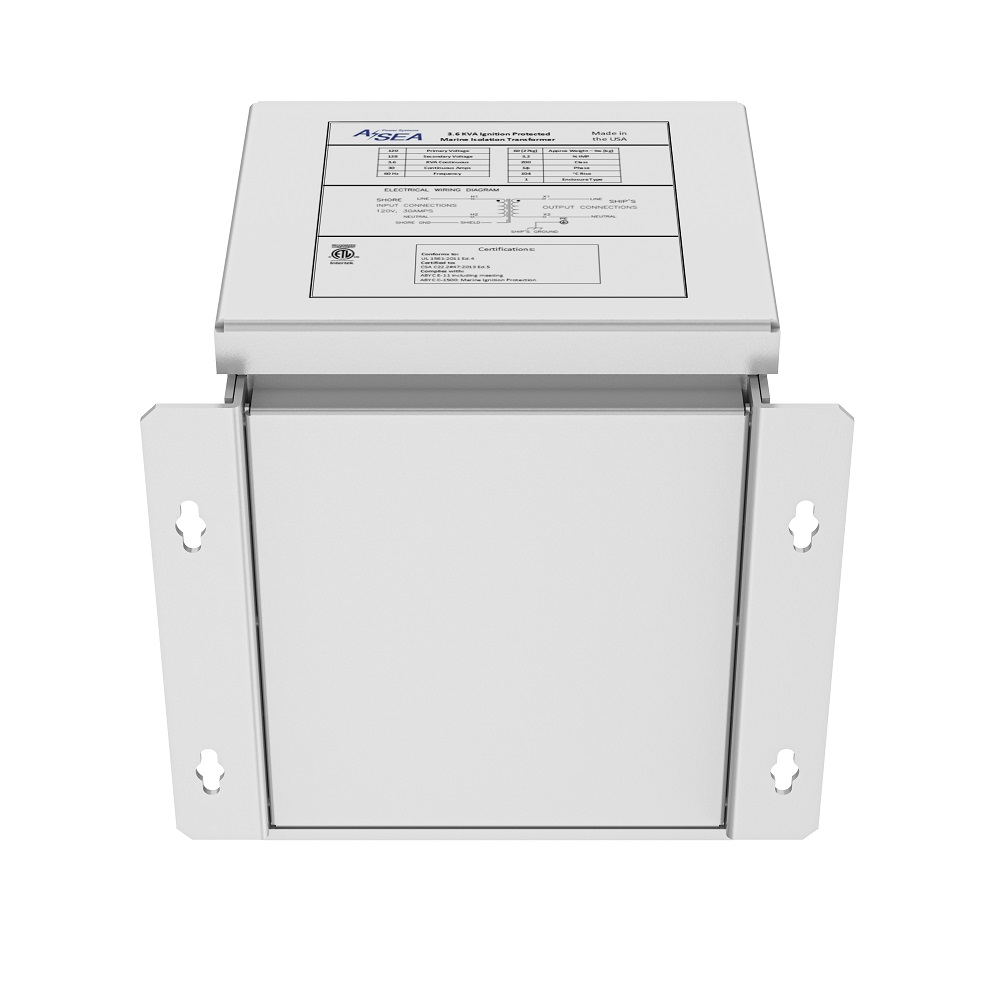
ASEA’s Isolation Transformer is designed to completely isolate a vessel’s electrical system from shore power, reducing corrosion and improving the performance of on-board equipment. It is installed in-line between the shore power inlet and the boat’s AC panel. The Isolation Transformer serves as a protective layer blocking stray currents from transferring between the shore and your vessel and preventing dockside ELCI tripping. It is commonly installed on center consoles and other gas-powered boats.
Features
- Ignition protected, safe for gasoline-powered vessels
- Complete Electrical Isolation, prevents dockside ELCI breaker trips
- Maintains a safer marine environment by mitigating the risk of ESD
- Ensures clean and stable AC power for on-board equipment
- Reduces galvanic corrosion
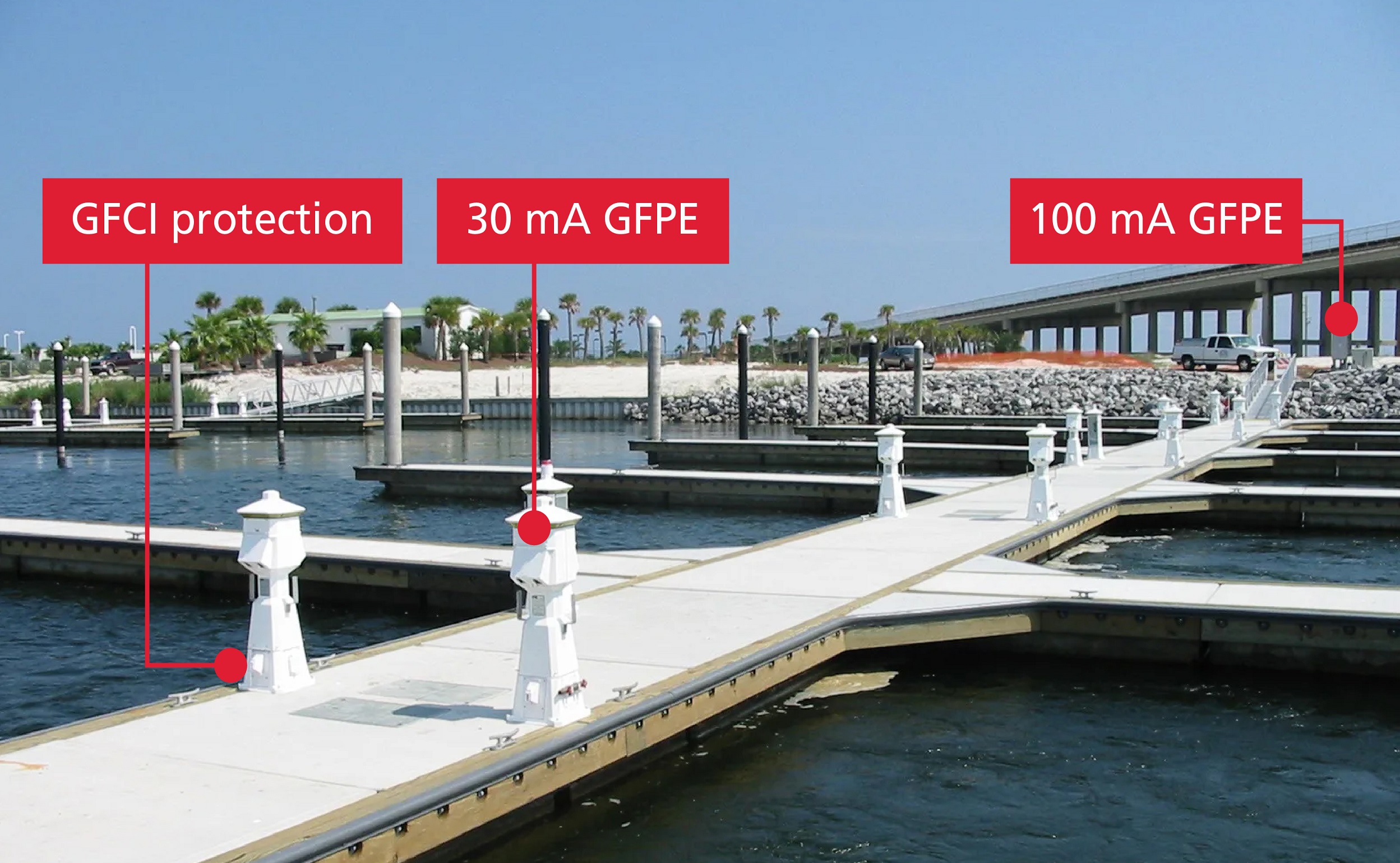
- Allows vessels to meet latest NEC 555.35 marina code that ensures GFPE limits are not exceeded
Certifications
- ABYC E-11 Compliant
- ABYC C-1500 (for ignition protection)
- UL 1561
COMMONLY INSTALLED ON
Ignition Protected
Galvanic Corrosion Protection

Charles IsoG2 Replacement
SPECIFICATIONS
| Model | 3.6 kVA | 12 kVA |
Input Voltage |
120 VAC |
248/240 V |
Input Current |
30 A |
50 A |
Output Voltage |
120 VAC |
240 VAC |
Output Current |
30 A |
50 A at 240 V input43 A at 208 V input |
Output Frequency |
60 Hz |
60 Hz |
Weight |
57 lb |
160 lbs |
Height |
21.6 cm / 8.5 in |
27 cm / 10.6 in |
Width |
21.6 cm / 8.5 in |
26 cm / 10.2 in |
Width (with flange) |
27.4 cm / 10.8 in |
33 cm / 13.0 in |
Depth |
26.7 cm / 10.5 in |
36 cm / 14.1 in |
How to Navigate hidden risks of Dock Power
Shore power can introduce stray currents, voltage fluctuations, and corrosion, impacting your boat’s electrical system. Read this blog to learn how to manage these risks.
Latest changes to NEC-555 standards
NEC 555.35 ensures marina electrical safety by detecting and interrupting unintended leakage currents. Understanding these regulations is key to avoiding shore power interruptions.
Toroidal vs Potted Isolation Transformer
Only potted transformers meet ABYC standards, ensuring protection against moisture, corrosion, and electrical hazards. Read this blog to learn why.
Choosing Isolation Transformer or Galvanic Isolator?
Every time your boat connects to shore power, it faces potential risks from galvanic corrosion and stray currents. The right protection depends on multiple factors.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is ignition protection, and why is it important?
Ignition protection ensures that electrical equipment will not produce a spark or high surface temperature that could ignite flammable gases in a confined space. The ASEA Isolation Transformer is certified to ABYC C-1500, UL 1500, and UL 1561 standards, making it safe for installation on gasoline-powered boats where ignition risk is a concern. This added layer of safety is critical in preventing onboard fires and ensuring compliance with marine safety regulations.
Is the ASEA Isolation Transformer toroidal or potted construction?
The ASEA Isolation Transformer is a potted transformer, meaning it is fully sealed within a protective enclosure. This design enhances durability, reduces noise and vibration, and improves heat dissipation, making it well-suited for marine environments. Unlike toroidal transformers, which do not meet ABYC compliance standards, potted transformers offer superior safety and longevity for onboard electrical isolation.
Which transformer design is better according to ABYC standards, toroidal or potted?
A toroidal transformer features a ring-shaped core, offering efficiency and compact design but lacking necessary safety measures for ABYC compliance. A potted transformer, like the ASEA Isolation Transformer, is fully sealed in a protective enclosure, making it significantly more durable, resistant to moisture and vibration, and compliant with ABYC E-11.7.1 standards. Because toroidal transformers do not provide adequate isolation for marine environments per ABYC guidelines, potted transformers are the superior choice for onboard safety and reliability.
What are the latest NEC 555.35 requirements for marina electrical safety?
The latest NEC 555.35 requirements focus on improving marina electrical safety by ensuring that ground fault protection devices (GFPEs) are set to appropriate trip limits. This reduces the risk of stray electrical currents entering the water, mitigating the chances of Electric Shock Drowning (ESD) and unintentional tripping of dockside ELCI breakers. Compliance with NEC 555.35 ensures that vessels and marinas operate within the highest safety standards. The ASEA Isolation Transformer meets the latest NEC 555.35 requirements.
How does an isolation transformer protect against galvanic corrosion?
Galvanic corrosion occurs when dissimilar metals in contact with water create an electrochemical reaction, leading to material degradation over time. The ASEA Isolation Transformer provides complete electrical isolation between shore power and the vessel’s onboard electrical system, eliminating the conductive path that allows galvanic currents to flow. This safeguards metal components, prolonging the lifespan of under-hull fittings, shafts, and propellers.
How should the ASEA Isolation Transformer be mounted and wired?
The ASEA Isolation Transformer supports both floor and wall mounting. When floor-mounted, the transformer should be positioned on a stable, vibration-resistant surface to ensure secure operation. For wall mounting, it must be fixed to a structurally sound bulkhead using appropriate fasteners to prevent movement in rough conditions. Wiring should follow ABYC standards, ensuring correct input and output connections, proper grounding, and adherence to vessel-specific electrical system requirements. It is recommended that installation be performed by a qualified marine electrician to ensure safety and compliance.










